Pedestrian fatalities increased by 13% in 2022, with over 7,500 deaths recorded according to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. Most accidents happen because people don’t follow basic safety protocols.
We at DriverEducators.com compiled the 10 road safety rules for pedestrians that can dramatically reduce your risk of injury. These proven strategies work when applied consistently in real-world situations.
Understanding Basic Pedestrian Traffic Laws
Pedestrians hold the right-of-way at all marked crosswalks and unmarked crosswalks at intersections, regardless of traffic signals according to federal traffic laws. Drivers must yield completely and stop well back from crosswalks to allow other drivers clear sight lines. However, pedestrians must yield to vehicles when they cross mid-block without designated crosswalks or signals. At intersections, pedestrians cannot enter roadways until they can safely cross to the other side without interference with vehicle traffic.
Sidewalk Usage Requirements
Federal law mandates pedestrians use sidewalks when available, and violations can result in fines that range from $50 to $200 in most states. When sidewalks don’t exist, pedestrians must walk on the left shoulder as far from vehicles as possible while they face traffic. Pedestrians who walk in roadways when sidewalks are present commit jaywalking in 47 states. Children under 10 cannot cross streets alone legally and require adult supervision at all times near traffic areas.

Traffic Signal Compliance Rules
Pedestrians must obey all traffic control signals, signs, and pavement markings when they cross streets. Those who cross against pedestrian signals receive jaywalking citations with fines between $75 and $300 (depending on state jurisdiction). The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration reports that 7,314 pedestrians were killed in traffic crashes in 2023, representing a 3.7-percent decrease from 2022. Repeat offenders face penalties that escalate, which include mandatory safety courses and potential license restrictions for drivers who frequently violate pedestrian laws.
Legal Consequences for Violations
Pedestrian law violations create liability issues in accident cases and potentially reduce compensation by 25% to 50% under comparative negligence rules. Insurance companies actively investigate pedestrian behavior during claims processing, and violations can void coverage entirely. States like California and New York impose additional civil penalties up to $1,000 for pedestrian infractions in school zones or construction areas.
These legal frameworks establish the foundation for pedestrian safety, but effective protection requires more than just knowledge of the law. The next section explores practical safety techniques that help pedestrians navigate traffic situations safely.
Essential Safety Practices for Walking Near Traffic
The stop-look-listen method is an important pedestrian safety practice according to traffic safety research, yet most adults skip this basic protocol. Stop completely at curb edges, look left-right-left while you scan for turning vehicles, and listen for engine sounds or horns before you step into roadways. Make direct eye contact with drivers before you cross and wait until vehicles come to complete stops, not just slow down. Never assume drivers see you, even at marked crosswalks where 74% of pedestrian fatalities occur outside intersection areas according to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration.
Visibility Tactics That Work
Wear bright colors during daylight hours and reflective materials after sunset, which help increase driver recognition distance. White or yellow clothing works best during day hours, while reflective vests or strips become essential after dark when 77% of pedestrian deaths happen. Cross streets only in well-lit areas and avoid walking during heavy rain or fog when visibility drops below 200 feet. Time your crossings when traffic gaps exceed 10 seconds (this gives drivers adequate reaction time at normal speeds).
Driver Blind Spot Awareness
Large vehicles create blind spots that extend 20 feet in front and 30 feet behind their cabs, which makes truck intersections particularly dangerous. Drivers who make right turns cannot see pedestrians positioned within 10 feet of their passenger side, while left-turning drivers focus on oncoming traffic rather than crosswalks. Position yourself where drivers can see you clearly before you enter their path, and never walk behind vehicles that reverse in parking lots or driveways.
Street Crossing Techniques
Choose crosswalks over mid-block crossings whenever possible, as marked crossings reduce accident risk by 40% compared to random street crossings. Wait for complete traffic stops before you enter crosswalks, even when you have the right-of-way signal. Walk at normal pace through crossings rather than run (sudden movements confuse drivers and increase accident probability). Keep your head up and maintain awareness of all traffic directions throughout the crossing process.

Modern technology offers additional tools that can enhance these traditional safe driving practices and provide extra protection for pedestrians in today’s complex traffic environment.
Technology and Tools for Pedestrian Safety
Google Maps and Apple Maps now include pedestrian-specific routes that prioritize sidewalks, crosswalks, and well-lit paths over the shortest distance routes. These apps reduce pedestrian exposure to high-traffic areas according to urban planning studies, though most people still use default directions when they walk. The Waze app provides real-time alerts about construction zones and traffic incidents that force pedestrians into dangerous detours. CitiMapper excels in dense urban environments by showing subway entrances, bus stops, and pedestrian bridges that keep walkers away from street-level traffic entirely.
Smart Wearables and High-Visibility Gear
LED armbands and ankle lights increase driver recognition distance to 500 feet compared to 125 feet for standard reflective tape according to National Safety Council tests. The Lumos helmet combines bike helmet protection with built-in LED lights and turn signals that pedestrians activate through handlebar controls or smartphone apps. Reflective vests with Class 2 ANSI ratings provide 360-degree visibility and cost under $15, yet only 8% of nighttime pedestrians wear any reflective gear. Smart watches like Apple Watch can detect car crashes and automatically call emergency services (though this feature works inconsistently for pedestrian accidents).
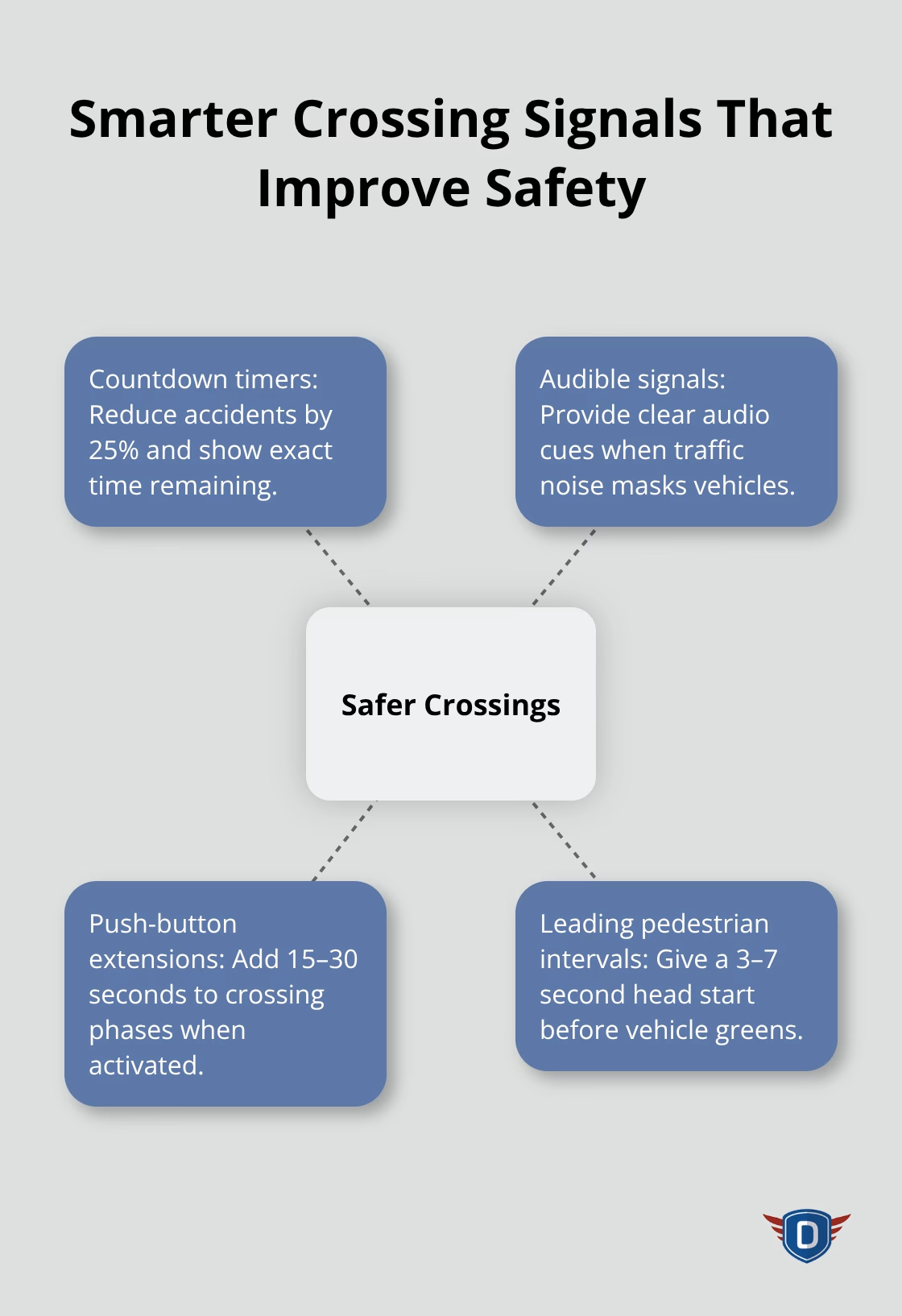
Advanced Crossing Signal Systems
Pedestrian countdown timers reduce accidents by 25% at intersections where they operate and give walkers precise information about remaining crossing time. Audible crossing signals benefit all pedestrians, not just those with visual impairments, by providing audio cues when traffic noise masks approaching vehicles. Push-button crossing systems extend pedestrian crossing phases by 15 to 30 seconds when activated (though many pedestrians ignore these buttons and cross during regular traffic cycles). Leading pedestrian intervals give pedestrians a 3 to 7 second head start before vehicles get green lights according to Federal Highway Administration data.
Emergency Response Technology
Smartphone emergency features like iPhone’s Emergency SOS and Android’s Emergency Location Service can automatically share precise location data with first responders during accidents. These systems work even when cellular service is weak and can save critical minutes in emergency response times. Personal safety apps like bSafe and SafeTrek allow pedestrians to alert emergency contacts or authorities with one-touch activation when they feel unsafe near traffic areas. Understanding what causes most car accidents helps pedestrians anticipate dangerous driver behaviors and choose safer routes and crossing times.
Final Thoughts
The 10 road safety rules for pedestrians outlined in this guide reduce accident risk by up to 40% according to traffic safety data. Legal compliance, visibility practices, and defensive walking create multiple layers of protection that work together effectively. Pedestrians who consistently use crosswalks, wear reflective gear, and maintain situational awareness experience significantly fewer traffic incidents than those who ignore basic protocols.
Defensive walking treats every intersection as potentially dangerous, regardless of traffic signals or right-of-way laws. Drivers often fail to see pedestrians, so you must verify eye contact before you cross and choose well-lit routes whenever possible. The 7,314 pedestrian fatalities in 2023 prove that safety protocols save lives when people apply them correctly (especially during nighttime hours when 77% of deaths occur).
Technology tools like smartphone apps and LED safety gear provide additional protection, but they supplement rather than replace basic safety practices. We at DriverEducators.com teach students to recognize and respect pedestrian rights through our driver education programs, which creates safer roads for everyone. Practice these safety principles consistently, and they become automatic responses that protect you in unexpected traffic situations.