Road construction zones present serious risks to both workers and drivers. The Federal Highway Administration reports that 857 people died in work zone crashes in 2020 alone.
We at DriverEducators.com believe proper safety protocols can prevent most of these tragedies. This guide covers proven practices that protect everyone on construction sites.
Worker Safety Protocols in Road Construction Zones
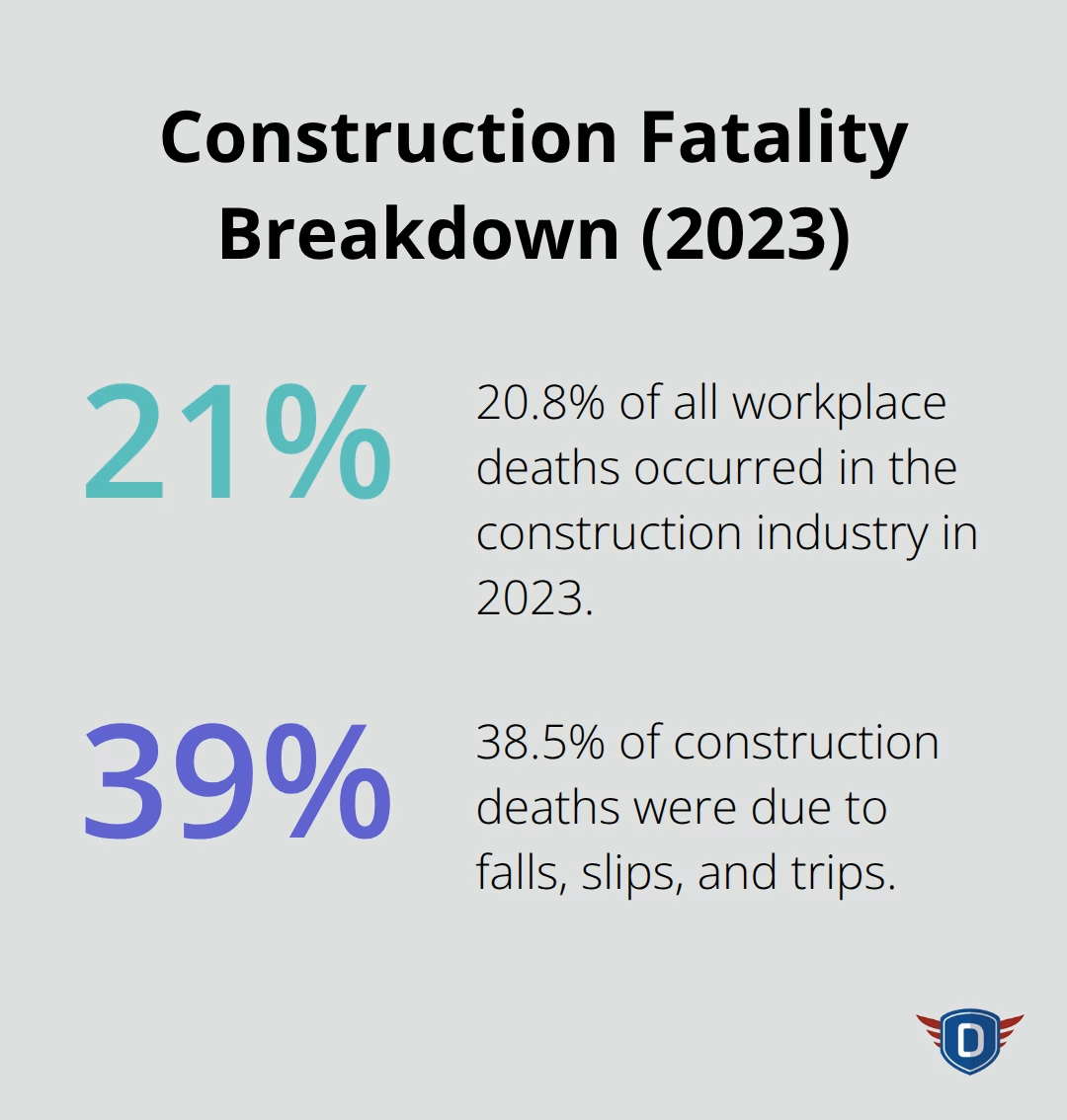
Road construction workers face significant workplace hazards, with about 1 in 5 (20.8 percent) workplace deaths occurring in the construction industry in 2023, and 38.5 percent of these deaths were due to falls, slips, and trips according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration mandates specific protective equipment that saves lives daily. High-visibility clothing rated ANSI Class 2 or 3 prevents struck-by incidents when workers remain visible from appropriate distances. Hard hats must meet ANSI Z89.1 standards and workers replace them every five years regardless of visible damage. Steel-toed boots with slip-resistant soles reduce foot injuries on uneven surfaces.
Safety glasses prevent eye injuries from debris and dust particles.
Traffic Control Saves Lives Through Proper Placement
Flaggers position themselves before work zones and face traffic at all times. The Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices establishes standards for traffic control devices including stop and slow paddles with retroreflective materials. Flaggers rotate regularly to maintain alertness since fatigue contributes to traffic control accidents. Two-way radio communication between flaggers prevents coordination failures that lead to head-on collisions. Night operations require additional equipment and flaggers must wear LED safety vests for enhanced visibility.
Heavy Equipment Operators Follow Strict Safety Standards
Equipment operators perform daily pre-operation inspections that identify mechanical failures before they cause accidents. Backup alarms audible from appropriate distances warn pedestrians of vehicles in reverse. Spotters guide operators in areas with limited visibility and maintain constant radio contact. Operators shut down equipment completely before they perform maintenance tasks since equipment-related fatalities often occur during improper service procedures. Rollover protective structures significantly reduce operator deaths when operators combine them with seat belt usage.
Communication Systems Prevent Fatal Accidents
Radio systems connect all team members across construction sites and prevent isolation incidents. Workers check radio functionality every morning and carry backup batteries for extended shifts. Emergency channels remain clear for urgent communications while routine traffic uses separate frequencies. Hand signals supplement radio communication when noise levels exceed safe hearing thresholds. Teams establish code words for immediate evacuation procedures that all workers memorize during safety orientation.
These safety protocols form the foundation for worker protection, but drivers also play a vital role in construction zone safety through their actions and defensive driving awareness.
Driver Safety Guidelines Through Construction Areas
Drivers who approach construction zones must reduce speed immediately when they see warning signs, not when they reach the actual work area. Speeding was a contributing factor in 29% of all traffic fatalities in 2023. Drop your speed by at least 10 mph below posted limits even before temporary speed reduction signs appear. Merge into open lanes as soon as warning signs indicate lane closures ahead rather than wait until the last possible moment. This zipper merge technique is the most effective method for merging two congested lanes and prevents aggressive behaviors that lead to rear-end collisions.
Extend Your Distance Behind Other Vehicles
Standard three-second distances become inadequate in construction areas where sudden stops happen frequently. Increase your distance to at least six seconds behind the vehicle ahead, particularly when you follow large trucks that block your view of hazards ahead.
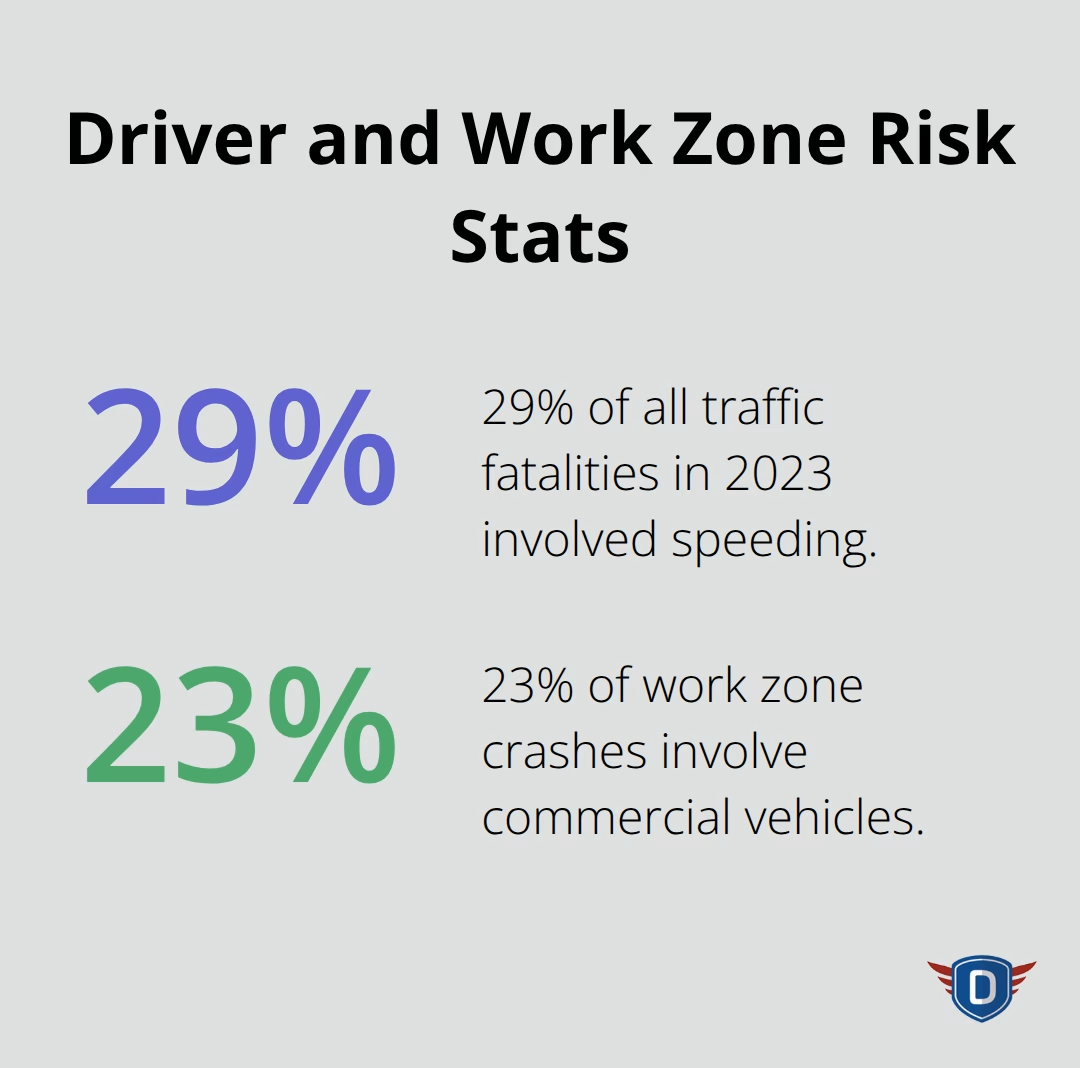
The Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration reports that 23% of work zone crashes involve commercial vehicles, often because passenger car drivers cannot see around trucks to anticipate traffic pattern changes. Watch for brake lights several cars ahead rather than just the vehicle directly in front of you. Construction zones create stop-and-go traffic patterns that catch inattentive drivers off guard.
Read Construction Signals Before Workers Act
Orange diamond-shaped signs indicate temporary conditions ahead while rectangular orange signs provide specific instructions for lane changes or speed reductions. Electronic message boards display real-time information about delays and alternate routes, but drivers often ignore these warnings until traffic comes to a complete stop. Flagger signals override all other traffic control devices (including traffic lights), so watch flaggers continuously rather than look at your phone or adjust radio settings. Construction workers depend on driver compliance with their signals since their safety equipment only protects them from certain types of impacts.
These driver behaviors work hand-in-hand with modern technology solutions that construction companies now deploy to create safer work environments for everyone on the road.
Technology and Equipment for Enhanced Construction Safety
Modern construction zones deploy sophisticated warning systems that alert drivers miles before they reach work areas. Electronic message boards positioned 2-3 miles ahead of construction sites display real-time information about delays, alternate routes, and lane closures. The Federal Highway Administration found that these advance warning systems help improve work zone safety, with work zone fatalities decreasing by 7 percent between 2021 and 2022 while overall roadway fatalities declined by 1.7 percent.

Automated flagger assistance devices replace human flaggers in high-speed corridors where vehicle speeds exceed 45 mph, which protects workers from struck-by incidents while traffic flow continues efficiently. Smart work zone systems use sensors to detect vehicles and automatically adjust signal timing based on real-time traffic conditions.
Concrete Barriers Outperform All Other Protection Methods
Temporary concrete barriers create positive protection between workers and traffic, providing effective protection against vehicle intrusions according to Transportation Research Board data. These barriers must extend at least 100 feet beyond the work area on both ends to account for errant vehicles that lose control before they reach the construction zone. Water-filled plastic barriers fail during high-speed impacts and offer inadequate protection for workers who operate heavy equipment. Steel plate barriers provide intermediate protection but require proper anchors to prevent displacement during impacts. Orange construction barrels serve as visual guides only and provide zero physical protection against vehicle intrusions.
Digital Communication Systems Coordinate Teams Instantly
Modern construction sites use mesh radio networks that maintain connectivity even when traditional cell towers experience outages. These systems allow supervisors to broadcast emergency alerts to all workers simultaneously rather than rely on individual radio calls that workers might miss. GPS-enabled communication devices track worker locations during evacuations and help emergency responders locate injured personnel quickly. Telematics systems in heavy equipment monitor operator behaviors and automatically alert supervisors when operators exceed safe speed limits or operate outside designated work areas. These technologies eliminate the communication delays that contribute to construction zone safety incidents.
Advanced Sensor Technology Prevents Equipment Accidents
Proximity sensors on heavy equipment detect workers within danger zones and automatically shut down machinery when personnel enter restricted areas. Backup cameras with audio alerts warn operators about obstacles and workers behind vehicles, which reduces struck-by incidents significantly. Load moment indicators prevent crane tip-overs by monitoring weight distribution and boom angles in real-time. These systems override operator controls when equipment approaches unsafe operating limits, which protects both operators and nearby workers from catastrophic equipment failures.
Final Thoughts
Road construction safety requires workers to follow protective equipment standards, drivers to reduce speeds and maintain proper distances, and construction companies to deploy modern warning systems. The 857 work zone fatalities in 2020 show that current safety measures need constant reinforcement and improvement. Regular safety training prevents complacency that leads to accidents.
Workers must refresh their knowledge of equipment operation procedures, while drivers need education about construction zone navigation. The 29% of traffic fatalities that involve speeding shows that awareness campaigns alone cannot change dangerous behaviors. Technology continues to advance road construction safety through automated systems that remove human error from traffic control.
Proximity sensors prevent equipment accidents, while mesh radio networks maintain communication during emergencies (these innovations work only when teams combine them with proper training and consistent safety protocols). We at DriverEducators.com teach defensive driving techniques that protect both students and construction workers. Road construction safety improves when all road users understand their responsibilities and follow established safety practices consistently.